ELSIセミナー
SEMINAR
September 21, 2016
Engineered Nucleoside/tide Kinases Synthesize the Nucleoside Triphosphates with Rearranged Watson-Crick Hydrogen Bonding Patterns....
- スピーカー
- Mariko Matsuura (University of Florida, US)
- 日付
- September 21, 2016
- 時間
- 11:00
- 場所
ELSI-1 Building - 102 ELSI Hall
Abstract
One of the most ambitious long-term goals of synthetic biology is the construction of living cells whose core biopolymers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) have molecular structures different from analogous biopolymers found universally in all life forms known on Earth.
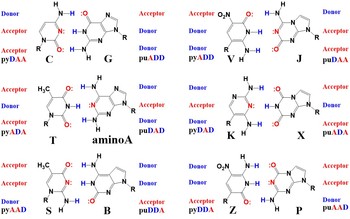
My Ph.D. work uses one of the Artificially Expanded Genetic Information Systems (AEGIS, Figure 1) developed by the Benner group [1]. The AEGIS contains nucleobases that resemble natural purines and pyrimidines, but have different hydrogen-bonding patterns. RNA polymerases, DNA polymerases, and reverse transcriptase accept the AEGIS nucleotides [2] [3]. Moreover, amplification and sequencing methods are developed for DNA and RNA containing the AEGIS [3] [4]. Therefore, the remaining step to obtain living cells that utilize the AEGIS-based biopolymers is to make the metabolisms that synthesize AEGIS nucleoside triphosphate in vivo [5]. My research is engineering nucleoside/tide kinases to phosphorylate the AEGIS nucleosides to obtain their corresponding triphosphates.
In this talk, the kinase screening methods and selected nucleoside/tide kinases that synthesize the AEGIS triphosphates will be introduced. Assay development and the relationships between kinase structures and specificities will be discussed.
References:
[1] Piccirilli, J.A., Krauch, T., Moroney, S.E. and Benner, S.A. (1990) Enzymatic incorporation of a new base pair into DNA and RNA extends the genetic alphabet. Nature 343, 33-37.
[2] Laos, R., Shaw, R., Leal, N.A., Gaucher, E. and Benner, S. (2013) Directed evolution of polymerases to accept nucleotides with nonstandard hydrogen bond patterns. Biochemistry 52, 5288-5294.
[3] Leal, N.A., Kim, H.J., Hoshika, S., Kim, M.J., Carrigan, M.A. and Benner, S.A., 2014. Transcription, reverse transcription, and analysis of RNA containing artificial genetic components. ACS Synth. Biol. 4, 407-413.
[4] Yang, Z., Chen, F., Alvarado, J.B. and Benner, S.A. (2011) Amplification, mutation, and sequencing of a six-letter synthetic genetic system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15105-15112.
[5] Matsuura, M.F., Shaw, R.W., Moses, J.D., Kim, H.J., Kim, M.J., Kim, M.S., Hoshika, S., Karalkar, N. and Benner, S.A., (2016) Assays to detect the formation of triphosphates of unnatural nucleotides: application to Escherichia coli nucleoside diphosphate kinase. ACS Synth. Biol. 5, 234-240.
Structure of the AEGIS nucleobases showing the hydrogen-bonding pattern, which differs from that of standard nucleotides.